Atomic spacing
Atomic spacing refers to the distance between the nuclei of atoms in a material. This space is extremely large compared to the size of the nucleus, because it is the strength of the bonds which make a material strong. The atomic spacing is usually determined by passing an electromagnetic wave of known frequency through the material, and using the laws of diffraction to determine its atomic spacing.
The frequency of an electromagnetic wave can be calculated using the formula:
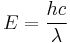
Rearranged to:
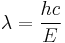
Where λ = Frequency,
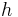 = Planck Constant (6.626068 × 10-34 m2 kg / s)
= Planck Constant (6.626068 × 10-34 m2 kg / s)
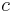 = The speed of light (299,792,458 m/s)
= The speed of light (299,792,458 m/s)
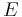 = The energy of a photon
= The energy of a photon